Outsmart 99% of People with AI | Boost Success & Productivity
Introduction
Most people are wasting AI’s potential. They open ChatGPT, type random questions, get generic answers, and wonder why everyone’s excited about this technology. Meanwhile, a smaller group is using AI systematically to reclaim hours every week, accelerate their learning, and produce higher-quality work in less time.
I stopped treating AI like a search engine and started building a system around it. That shift changed everything.
I’m talking about reclaiming 10-15 hours monthly, making better decisions with less mental strain, and producing higher-quality work in half the time. Not because I found secret prompts or special tools—but because I built repeatable workflows that turn AI from an occasional helper into a genuine productivity multiplier.
Here’s what I’ve learned: the difference between people getting amazing results with AI and those getting nowhere isn’t intelligence or technical skill. It’s having a system.
In this guide, I’m sharing that complete system with you:
- How to communicate with AI effectively (not just ask questions)
- How to build workflow systems that integrate AI daily
- Templates and automations that save hours weekly
- Advanced techniques that create competitive advantages
- Common mistakes to avoid (I made them so you don’t have to)
This guide is for you if:
- You’re a professional who wants to work smarter, not just harder
- You feel overwhelmed by competing demands on your time
- You’re curious about AI but unsure where to actually start
- You’re already using AI but not seeing the results you expected
What this isn’t:
- A course trying to sell you something
- Hype about AI replacing your job
- Vague advice about “embracing the future”
- Technical explanations of how AI actually works
I’ve spent the last year testing, refining, and systematizing these approaches. Some things worked brilliantly. Others failed completely. I’m giving you what actually works—the practical frameworks that deliver measurable results.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a complete AI productivity system: the prompts, workflows, automations, and quality controls that I use daily and that you can implement starting today.
The best time to build these skills was six months ago. The second best time is now.
Let’s get to work.
Master AI Productivity: A Practical Guide
1. Why AI Matters for Your Career Right Now

We’re at an inflection point. AI tools went from experimental novelty to critical workplace skill in roughly 18 months. The gap between people who use these tools systematically and those who don’t is widening every week.
Consider two professionals in similar roles:
Person A spends 6 hours weekly writing email campaigns, manually scheduling meetings, and creating reports from scratch.
Person B uses AI to handle these tasks in 45-90 minutes, redirecting those saved hours to strategy, relationship-building, and high-value work.
Within six months, Person B is getting promoted. Person A is wondering why opportunities pass them by.
The difference isn’t intelligence or work ethic—it’s adaptation speed.
Three Ways AI Creates Competitive Advantage

Speed Multiplication Tasks that once took hours now take minutes. I personally reclaimed approximately 10-15 hours monthly by systematizing weekly planning, email responses, and meeting preparation. That’s roughly 2-3 extra work weeks annually to invest in growth, learning, or personal time.
Better Decision-Making We make hundreds of micro-decisions daily while mentally exhausted. Should I respond to this email now? What’s the best approach for this project? Which task deserves priority?
AI removes the cognitive load from repetitive decisions. You can analyze options, weigh trade-offs, and simulate outcomes without decision fatigue clouding your judgment.
Accelerated Learning AI functions as an always-available tutor that adjusts to your level, answers questions without judgment, and provides immediate feedback. Skills that traditionally took months to learn can be acquired in weeks with the right AI-assisted approach.
The Cost of Waiting
If you’re not building AI skills now, you’re not maintaining your position—you’re falling behind. Your competition isn’t just the person in the next office. It’s someone using AI to accomplish in 2 hours what takes you 8.
The good news? We’re still early. Most people are in the “random ChatGPT questions” phase. They haven’t built systems or integrated AI into daily workflows. This is your window to gain an advantage rather than just catching up later.
2. How to Communicate with AI: Master Prompts and System Design

Most people treat AI like a search engine: type a question, get an answer, repeat. This approach gets mediocre results and explains why so many people are underwhelmed by AI.
Effective AI communication requires structure, context, and specificity. Think of it like giving directions to a brilliant assistant who knows nothing about your life. “Drive me somewhere nice” won’t work. “Drive me to the Italian restaurant on 5th Street with the outdoor patio” will.
2.1 Understanding Prompt Types
Five core prompt types cover most practical applications:
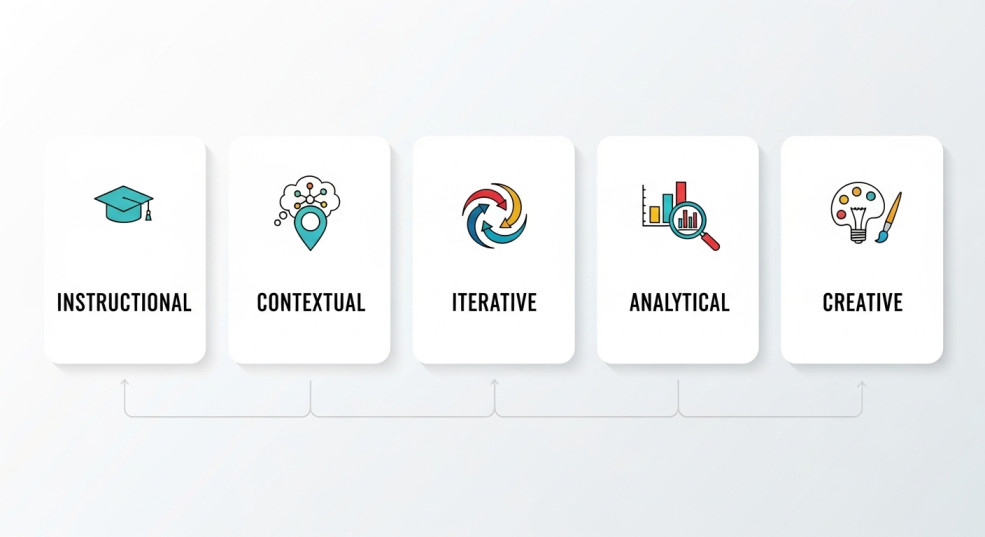

| Prompt Type | Purpose | Example |
| Instructional | Direct tasks with clear outcomes | “Write a 300-word LinkedIn post about AI in marketing, targeting CMOs, using a conversational but professional tone” |
| Contextual | Complex requests needing background | “I’m a freelance designer pitching to a tech startup that values innovation and speed. Write a proposal intro emphasizing these points while addressing their likely budget concerns” |
| Iterative | Refining outputs | “Make this 30% shorter,” “Add specific metrics,” “Adjust tone to be more enthusiastic” |
| Analytical | Breaking down information or decisions | “Analyze the pros and cons of launching my product now vs. waiting 3 months. Consider market conditions, my current resources, and competitive timing” |
| Creative | Generating ideas | “Give me 15 unique angles for a blog post about remote work productivity that haven’t been covered extensively” |
The Core Rule: Always include role, context, and desired format in your prompts.
Weak prompt: “Explain machine learning.”
Strong prompt: “You’re a data scientist explaining to a marketing professional with no technical background. Explain machine learning in 200 words using real-world marketing examples. Use short paragraphs, no jargon.”
The difference is clarity. The second prompt gives AI everything needed to deliver useful results immediately.
2.2 Master Prompts: Teaching AI About You
A master prompt is your AI’s instruction manual about you. Instead of re-explaining who you are and what you need in every conversation, you provide this context once.
What to Include:
- Your Background & Role: Your industry, expertise level, and professional focus
- Your Goals: Immediate objectives and longer-term direction
- Your Style Preferences: How you communicate and want information delivered
- Your Constraints: Time, budget, resources, technical skills
Master Prompt Template:
I’m [role/profession] with [experience level] in [industry/field]. My primary focus is [main work area].
My current goals: [list 2-3 specific goals]
Communication preferences: [tone, style, format—direct, detailed, casual, formal, etc.]
My constraints: [time, budget, skills, resources]
When I ask questions, assume this context unless specified otherwise. Tailor responses to my background, goals, and preferences.
Real Example:
I’m a content strategist with 5 years of experience working with B2B tech companies. My primary focus is thought leadership and SEO-driven content.
My current goals: Scale my freelance business to consistent $12K monthly revenue, systematize content workflows, land 3-5 retainer clients.
Communication preferences: Direct, actionable advice with real examples. Skip theory and fluff. Conversational but professional language. Step-by-step frameworks I can implement immediately.
My constraints: Solo operation with limited tool budget. No coding skills. Available work time is 25-30 hours weekly.
Save this in a note-taking app and paste it at the start of important conversations. Update quarterly as your situation evolves.
2.3 System Prompts: Defining AI Behavior
While master prompts tell AI about you, system prompts tell AI how to operate.
System prompts control:
- Tone & Voice: Formal or casual? Enthusiastic or measured?
- Depth & Detail: High-level overview or deep dive?
- Structure & Format: Paragraphs, lists, tables?
- Constraints & Boundaries: What to avoid, what requires extra care
System Prompt Example:
You are an expert content strategist with 15+ years of experience, specializing in actionable, data-driven strategies for B2B companies.
When responding:
– Use professional but conversational tone
– Provide specific, tactical recommendations with reasoning
– Structure advice in clear frameworks or step-by-step processes
– Include real-world examples when possible
– State assumptions clearly
– Avoid vague advice—every recommendation should be actionable
– End complex responses with a brief “Next Steps” summary
Constraints:
– Don’t recommend expensive solutions without budget-friendly alternatives
– Don’t use buzzwords without explaining them
– Customize everything to the provided context
Use system prompts for complex projects requiring consistent quality, specialized expertise, or collaborative work over multiple sessions.
2.4 Custom Instructions: Permanent AI Settings
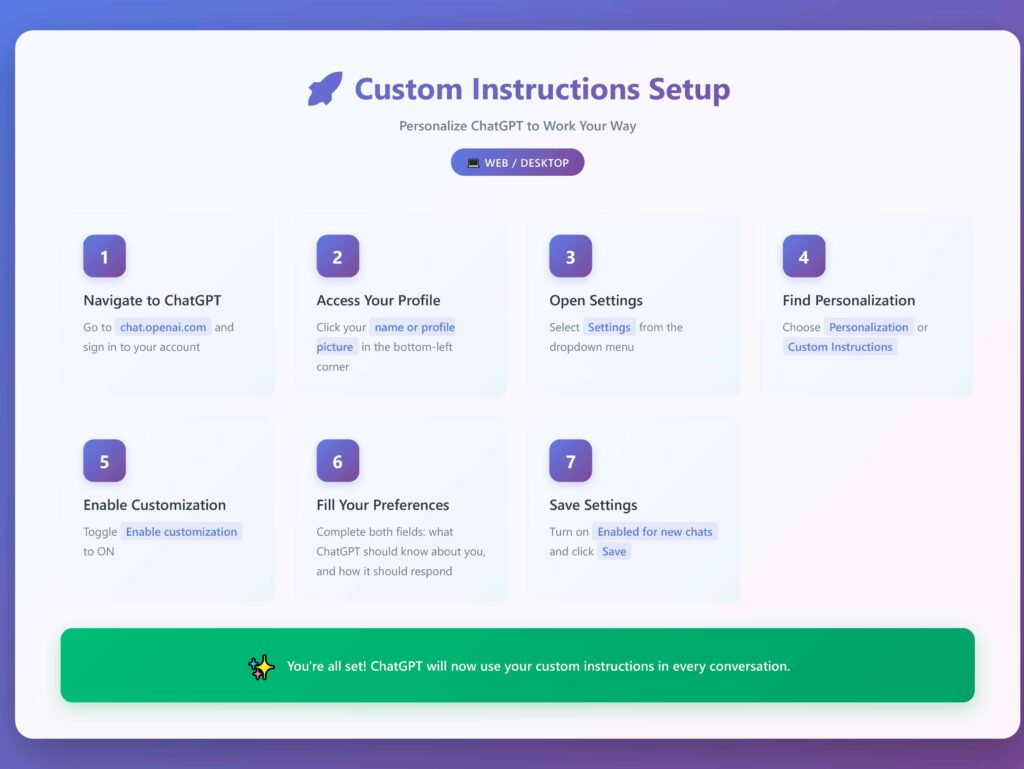

Most major AI tools (ChatGPT, Claude, etc.) allow you to set permanent preferences that apply to every conversation. This eliminates the need to paste your master prompt repeatedly.
Set Up Custom Instructions in Two Parts:
Part 1: What should AI know about you? Your background, context, and goals. Keep it concise but informative.
Example: “I’m a content strategist helping B2B tech companies grow through strategic content. I value efficiency, data-driven decisions, and practical frameworks over theory.”
Part 2: How should AI respond? Your style preferences, format needs, and specific requirements.
Example: “Be direct and actionable. Use conversational language but maintain professionalism. Explain reasoning behind advice. Format responses with clear headings and bullet points. Avoid clichés and obvious statements. If you need more context, ask specific questions rather than giving generic advice.”
Time Savings: If you use AI 10 times daily and save 2 minutes per conversation by not providing context, that’s 20 minutes daily or roughly 120 hours annually—just from spending 10 minutes on this setup once.
3. Building Your AI Workflow System

Knowledge without implementation is entertainment. This section transforms concepts into a practical system.
3.1 Audit Your Daily Tasks
Before automating anything, identify what’s consuming your time.
3-Day Task Tracking Exercise:
Track every task for three days. Record:
- What’s the task?
- How long did it take?
- How often do you do this? (daily, weekly, monthly)
- Could AI help? (yes/no/maybe)
After three days, analyze your list using these criteria:
High-Impact Automation Candidates:
- ✅ Repetitive (done more than once weekly)
- ✅ Time-consuming (30+ minutes per instance)
- ✅ Follows patterns (creative but structured)
- ✅ Cognitively draining but not strategic
Priority Scoring:
- High impact: Saves 1+ hour weekly
- Medium impact: Saves 30-60 minutes weekly
- Low impact: Saves less than 30 minutes weekly
Focus on high-impact tasks first. Don’t try automating everything simultaneously—pick your top 3 time-wasters and systematize those before moving to the next batch.
3.2 Map Tasks to AI Tools
You don’t need dozens of tools. 5-7 core tools handle 90% of work.
Essential AI Toolkit:
| Task Category | Recommended Tools | Primary Uses |
| Content Creation | ChatGPT, Claude, Jasper | Blog posts, emails, social media, ad copy |
| Meeting Management | Otter.ai, Fathom, Fireflies | Transcription, notes, action items |
| Project Planning | Notion AI, ClickUp AI | Task management, documentation, workflows |
| Time Optimization | Reclaim, Motion | Calendar blocking, focus time protection |
| Research & Analysis | ChatGPT, Perplexity | Market research, competitor analysis, synthesis |
| Automation | Zapier AI, Make | Connecting tools, workflow triggers |
| Communication | Grammarly, ChatGPT | Email polish, message drafting |
Practical Task Mapping:
Email Management:
- Draft responses → ChatGPT with custom instructions
- Polish drafts → Grammarly
- Schedule sends → Zapier automation
Content Creation:
- Brainstorm topics → ChatGPT creative prompts
- Create outlines → Notion AI
- Write first drafts → ChatGPT or Claude
- Edit and refine → Grammarly + manual review
Meeting Workflow:
- Auto-record meetings → Fathom or Fireflies
- Generate summaries → AI transcription tools
- Extract action items → ChatGPT analysis
- Schedule follow-ups → Reclaim or Motion
Each task has a specific tool assigned. This isn’t random jumping between platforms—it’s a system.
3.3 Create Reusable Prompt Templates

Templates standardize excellence. Once you create a prompt that produces great results, save it and reuse it forever.
Template Library Structure:
Content Creation Templates:
- Blog post outline generator
- Social media post creator
- Email newsletter framework
- Video script structure
Business Communications:
- Client proposal template
- Follow-up email sequences
- Meeting prep summary
- Project status update
Analysis & Strategy:
- Competitor analysis framework
- Content performance review
- Decision-making matrix
- Goal planning prompt
How to Build Your First Template:
Step 1: Write your best prompt for a frequent task.
Example for outreach emails:
Write a personalized outreach email to [prospect name] who is [their role] at [company]. They recently [specific action or achievement]. I want to [your goal]. Mention [specific value proposition]. Keep it under 150 words, friendly but professional tone.
Step 2: Test it 3-5 times with different scenarios. Refine until it consistently produces good results.
Step 3: Create a fill-in-the-blank version:
Write a personalized outreach email to [PROSPECT NAME] who is [THEIR ROLE] at [COMPANY]. They recently [SPECIFIC ACTION/ACHIEVEMENT]. I want to [YOUR GOAL]. Mention [VALUE PROPOSITION]. Keep it under [WORD COUNT] words, [TONE] tone.
Step 4: Save it somewhere accessible (Notion, Google Docs) with tags for easy searching.
Every time you create a prompt that produces exceptional results, immediately save it as a template. Within 3 months, you’ll have 30-50 templates handling most recurring tasks.
3.4 Set Up Automation Triggers
Automation triggers are “if this, then that” rules making AI work without manual prompting.
Real Automation Examples:
Email Automation:
- When email arrives with “urgent” in subject → Auto-flag and draft response → Send notification
- When you star an email → Auto-create task with AI-generated action items
Content Creation:
- When you save article to research folder → AI summarizes key points → Adds to Notion database
- When blog post publishes → AI generates 5 social posts → Schedules across platforms
Meeting Management:
- When meeting ends → AI transcribes → Extracts action items → Creates assigned tasks → Sends summary email
Time Management:
- Every Monday 8 AM → AI analyzes weekly calendar → Identifies conflicts → Suggests optimization → Blocks focus time
How to Set Up (No Coding Required):
- Choose your trigger (what starts the automation)
- Choose your action (what AI does)
- Test it a few times
- Let it run
Start With These Three:
Automation #1: Meeting Notes
- Trigger: Meeting ends
- Action: Transcribe → Summarize → Email attendees
- Tool: Fireflies + Zapier
Automation #2: Email Response Drafts
- Trigger: Specific emails received
- Action: Generate draft response → Save to drafts
- Tool: ChatGPT + Gmail integration
Automation #3: Daily Planning
- Trigger: 8 AM every weekday
- Action: Review tasks → Prioritize → Block calendar
- Tool: Reclaim + ClickUp AI
Start with one automation. Let it run for a week. Refine it. Then add the next one. Trying to set up 10 automations simultaneously creates frustration and abandonment.
Next Up: In the following sections, we’ll cover specific use cases, advanced techniques like custom GPTs, and how to avoid common pitfalls that undermine AI effectiveness.
4. Practical Use Cases: Where AI Delivers Results
Theory matters less than application. Here’s how to use AI for specific high-value tasks.
4.1 Time Management & Calendar Optimization

Weekly Calendar Review
Every Sunday evening, use this prompt:
Review my upcoming week’s calendar [paste schedule].
Identify:
1. Where I’m overcommitted
2. Gaps too small for productive deep work
3. Meetings that could potentially be emails or async updates
4. Optimal times for high-focus tasks based on meeting density
Suggest a restructured calendar maximizing deep work time.
The AI spots patterns you’d miss and suggests changes that can reclaim 4-6 hours of quality work time weekly.
Pair this with tools like Reclaim or Motion to automatically block focus time, reschedule tasks when meetings get added, and protect priorities from calendar creep.
Morning Task Prioritization
Every morning, dump your task list into ChatGPT:
Here are my tasks for today [list everything].
My top goal this week is [specific goal]. I have [X] productive hours available.
Which tasks should I tackle, in what order, and why? Identify anything I should delegate or postpone.
This considers effort, impact, dependencies, and your stated priorities—delivering a ranked list with reasoning in under 2 minutes. It eliminates decision fatigue and scattered focus.
Focus Session Design
Before deep work sessions:
I need to [specific task]. I have [time available].
Design a focus session including:
– 5-minute warm-up activity
– Work structure with strategic breaks
– Specific milestones to hit
– Success metrics
Base structure on Pomodoro or flow state principles.
Having a battle plan instead of wandering into work sessions can noticeably improve output quality.
4.2 Content Creation at Scale

Blog Post Production
Step 1 – Topic Generation:
Generate 15 blog post ideas for [target audience] about [general topic].
For each idea:
– Title (compelling and specific)
– Unique angle (what makes this different from existing content)
– Key takeaway readers will gain
Focus on practical, actionable topics with clear value propositions.
Step 2 – Outline Creation:
Create a detailed outline for: [chosen topic]
Target audience: [specific description]
Goal: [what readers should be able to do after reading]
Word count: [target length]
Include:
– Hook opening
– 3-5 main sections with subpoints
– Practical examples for each section
– Clear call-to-action
Identify where data, quotes, or case studies would strengthen arguments.
Step 3 – First Draft:
Write the [Introduction/Section Name] based on this outline: [paste outline]
Requirements:
– Conversational but professional tone
– Short paragraphs (2-4 sentences)
– Include specific example in [context]
– Open with a hook that addresses [pain point]
Word count: approximately [X] words
Work section by section. This maintains quality and gives you control over each part.
Step 4 – Refinement: After generating the full draft, use iterative prompts:
- “Make the introduction 30% shorter without losing the hook”
- “Add a concrete example in section 3”
- “Adjust tone to be more encouraging and less prescriptive”
Email Sequence Development
Create a 5-email welcome sequence for new subscribers to [your business/newsletter].
Context:
– Target audience: [description]
– Main value proposition: [what you offer]
– Goal: [build trust, drive first purchase, establish expertise, etc.]
For each email:
– Subject line (A/B test option)
– Email body (150-200 words)
– Clear CTA
– Timing (when in sequence)
Maintain consistent voice: [your brand voice description]
Social Media Content Calendar
Create a 2-week social media content calendar for [platform].
Topics to cover: [list 3-5 themes]
Target audience: [description]
Goal: [awareness, engagement, lead generation]
For each post:
– Core message
– Hook/opening line
– Key points (2-3)
– Call-to-action
– Optimal posting time
– Relevant hashtags (3-5)
Vary post types: educational, behind-the-scenes, thought leadership, user engagement.
4.3 Research & Learning Acceleration
Mastering New Skills
Use this progressive learning framework:
Session 1 – Landscape Overview:
Give me a high-level overview of [topic/skill].
Map the landscape:
– Core concepts I need to understand
– How these concepts relate to each other
– Common misconceptions beginners have
– Why this skill matters in [your field]
Keep it to 300 words. Don’t go deep yet—I need the big picture first.
Session 2 – Deep Dive:
Teach me [specific concept] in detail.
My background: [your relevant experience]
My goal: [what you want to achieve with this skill]
Structure:
1. Core concept in simple terms with an analogy
2. Key components broken down
3. Real-world application in [your field]
4. Common mistakes to avoid
5. One immediate practice exercise
Use examples relevant to [your industry/interest].
Session 3 – Application:
Show me 5 real-world scenarios where I could apply [skill/concept] in my work as [your role].
For each scenario:
– Situation description
– How to apply the skill step-by-step
– Expected outcome
– Potential pitfalls
Session 4 – Knowledge Testing:
Quiz me on [topic] with 5 progressively harder questions.
Wait for my answer to each question before providing feedback.
After the quiz, identify:
– Concepts I’ve mastered
– Areas needing review
– Recommended next learning steps
This systematic approach can compress learning timelines significantly compared to traditional courses.
Rapid Research & Analysis
Single Source Summary:
Summarize this article [paste content or URL if AI can access it].
Extract:
– Main argument/thesis
– 3-4 key supporting points
– Important data or statistics
– Conclusions
– Notable gaps or limitations
– How this relates to [your specific interest]
Keep under 250 words.
Multi-Source Synthesis:
Compare these three sources on [topic]: [paste excerpts or descriptions]
Identify:
– Where they agree
– Where they disagree
– Unique insights from each
– Which appears most credible and why
– Synthesized understanding incorporating all three
Present as: Consensus findings, Conflicting viewpoints, Recommended interpretation.
4.4 Business Strategy & Decision-Making
Strategic SWOT Analysis
Conduct a SWOT analysis for [your business/project].
Context:
– Current situation: [brief description]
– Market: [your market/industry]
– Goals: [your objectives]
For each quadrant (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats):
– Identify 5-6 points
– Explain why each matters
– Rate importance (Critical/High/Medium)
Then synthesize:
– Top 3 strategic priorities based on this analysis
– Quick wins to pursue immediately
– Risks requiring mitigation plans
Competitor Analysis Framework
Analyze [competitor name] as a competitor to [your business].
Evaluate:
– Market positioning and messaging
– Product/service offerings and pricing
– Marketing channels and tactics
– Apparent strengths and weaknesses
– Market gaps they’re not addressing
Suggest:
– 3 differentiation opportunities for us
– 2 defensive moves to protect our position
– 1 competitive advantage we can emphasize
Be specific with recommendations, not generic strategy advice.
Decision Matrix for Complex Choices
I’m deciding between [Option A] and [Option B].
Context: [describe your situation]
For each option, analyze:
– Pros and cons (prioritized by impact)
– Required resources (time, money, people)
– Risks and potential mitigation strategies
– Expected outcomes (realistic range)
– Alignment with my goals: [list your goals]
– Opportunity cost
Recommend which option and explain reasoning. Also identify what additional information would strengthen this decision.
Revenue Projection Modeling
Create a 12-month revenue projection for [business/product].
Current metrics:
– Monthly revenue: [amount]
– Customer acquisition cost: [amount]
– Average customer value: [amount]
– Current growth rate: [percentage]
Assumptions:
– Pricing strategy: [details]
– Planned marketing spend: [amount]
– Expected churn rate: [percentage]
Build:
– Monthly revenue projections
– Best case/base case/worst case scenarios
– Key drivers affecting outcomes
– Break-even analysis
– Sensitivity analysis (what happens if [key variable] changes by ±20%)
4.5 Email & Communication Management
Email Response Templates
Draft a response to this email: [paste email]
My situation:
– Relationship to sender: [colleague, client, prospect, etc.]
– Key points I need to address: [list]
– Tone: [professional, warm, apologetic, enthusiastic, etc.]
– Desired outcome: [what you want to happen next]
Keep under 150 words. Include clear next step or CTA.
Meeting Preparation Brief
I have a meeting about [topic] with [attendees/roles].
Meeting goal: [what needs to be accomplished]
My role: [your position/responsibility]
Create a meeting prep brief:
– Key discussion points (prioritized)
– Questions to ask
– Potential objections and responses
– Information I should have ready
– Desired outcomes and next steps
– Time allocation suggestions for a [X]-minute meeting
Difficult Conversation Framework
Help me prepare for a difficult conversation about [situation].
Context:
– The issue: [describe problem]
– Person involved: [their role and relationship to you]
– Stakes: [why this matters]
– Desired outcome: [what you hope to achieve]
Provide:
– Opening statement (sets tone without blame)
– Key points to communicate (focused on facts and impact)
– Anticipated resistance and how to address it
– Questions to ask that encourage dialogue
– Possible compromises or solutions
– How to end constructively regardless of outcome
5. Advanced Techniques

Once you’ve mastered the basics, these advanced approaches separate competent AI users from power users.
5.1 Super Prompts: Layered Instructions
A super prompt isn’t just detailed—it’s comprehensively layered with context, role definition, format requirements, constraints, and success criteria.
The Super Prompt Framework:
CONTEXT: [Who you are, your situation, relevant background]
ROLE: [What expert role you want AI to embody]
TASK: [Specific deliverable you need]
FORMAT: [Exact structure for the output]
CONSTRAINTS: [What to avoid, limitations, requirements]
TONE: [Communication style]
SUCCESS CRITERIA: [What makes this output excellent vs. mediocre]
Real Example – Content Strategy Super Prompt:
CONTEXT: I’m a SaaS marketing director for a B2B project management tool. Our target customers are operations managers at 50-500 person companies. We’re struggling with content differentiation—our blog sounds like everyone else’s.
ROLE: You’re a senior content strategist with 15 years specializing in B2B SaaS differentiation and thought leadership.
TASK: Create a content differentiation strategy for Q2 that establishes unique voice and angles.
FORMAT:
– Executive summary (3-4 sentences)
– Current content audit insights (bullet points)
– 3 differentiation opportunities with examples
– 5 specific content pieces to produce with angles
– Measurement framework (3-4 KPIs)
CONSTRAINTS:
– Budget: $5K/month for freelance support
– Team: 1 content manager, 1 designer
– Production capacity: 2 long-form pieces + 8 social posts weekly
– No budget for major tool investments
TONE: Strategic and direct. Speak like an experienced advisor to a peer, not a consultant pitching services.
SUCCESS CRITERIA: The strategy should be immediately actionable, clearly differentiated from generic “best practices” advice, and realistic given our constraints. Every recommendation should include the “why” behind it.
This level of specification produces dramatically better outputs than generic requests.
When to Use Super Prompts:
- Complex projects requiring multiple considerations
- High-stakes deliverables (client work, important presentations)
- When you need AI to think through problems deeply, not just respond quickly
- Collaborative work spanning multiple sessions
Building Your Super Prompt Library:
- Identify your 5 most important recurring complex tasks
- Spend 20-30 minutes crafting a super prompt for each
- Test 3-5 times and refine based on outputs
- Save with clear naming: “SUPER_[Category]_[Specific Use]”
- Review and update quarterly
5.2 Custom GPTs & AI Agents

Custom GPTs (or similar features in other AI platforms) are specialized AI assistants trained for specific roles. Instead of starting from scratch each time, your custom GPT already knows your context, preferences, and requirements.
When to Build a Custom GPT:
- ✅ Repetitive specialized work in a specific domain
- ✅ Need for consistent quality across multiple interactions
- ✅ Complex workflows following the same pattern
- ✅ Team collaboration requiring shared AI assistance
Don’t Build Custom GPTs For:
- ❌ One-off tasks
- ❌ General questions that change constantly
- ❌ Tasks where you’re still experimenting with approach
How to Create a Custom GPT (Step-by-Step):
Step 1: Define the Purpose Be narrow and focused. “Content helper” is too broad. “LinkedIn thought leadership post creator for B2B SaaS executives” is focused.
Step 2: Build Comprehensive Instructions
You are a [specific role/expert type].
Your expertise: [specific knowledge domains]
My background:
– Role: [your position]
– Industry: [your field]
– Goals: [your objectives]
– Constraints: [your limitations]
When responding, always:
– [Specific behavior 1]
– [Specific behavior 2]
– [Specific behavior 3]
Never:
– [Thing to avoid 1]
– [Thing to avoid 2]
Output format:
– [Preferred structure]
– [Length guidelines]
– [Style requirements]
Communication style: [tone description]
Step 3: Upload Knowledge Base

Include:
- Past work samples showing your style
- Industry reports or research you reference frequently
- Templates and frameworks you use regularly
- Company information, brand guidelines, etc.
- Process documentation
Step 4: Create Conversation Starters
Write 4-6 prompts representing your most common use cases. These make the GPT immediately useful and guide others if you share it.
Examples:
- “Create a LinkedIn post about [topic] following my standard format”
- “Analyze this campaign performance data and recommend optimizations”
- “Draft a client proposal for [situation] using our standard structure”
Step 5: Test Extensively
Run it through 10-15 real scenarios before relying on it. Compare outputs to what you’d create manually. Refine instructions based on gaps.
Step 6: Iterate Monthly
As you use it, you’ll discover improvements. Treat your custom GPT as a living tool that gets better over time.
Example Custom GPT Use Cases:
“Content Chief” GPT:
- Trained on your writing samples and style guide
- Knows your target audiences and their pain points
- Understands your SEO strategy and keyword targets
- Has templates for outlines, drafts, and social posts
- Can analyze competitor content and suggest improvements
“Strategy Advisor” GPT:
- Loaded with your business model and market context
- Trained on frameworks you use (SWOT, Jobs-to-be-Done, etc.)
- Knows your constraints (budget, resources, timeline)
- Gives strategic advice specific to your situation
“Client Communication” GPT:
- Has your communication style and tone preferences
- Knows common client scenarios and appropriate responses
- Understands your services, pricing, and boundaries
- Drafts emails, proposals, and follow-ups in your voice
Pro Tip: Start with ONE custom GPT for your single most time-consuming repetitive task. Master that before building more. Better to have one excellent assistant than five mediocre ones you rarely use.
5.3 Validation & Quality Control
AI makes mistakes. It hallucinates facts with complete confidence. If you’re using AI for anything important, you need validation systems.
The Golden Rule: AI Proposes, Human Validates
Never publish AI-generated content without review. Never make business decisions solely on AI analysis. Never present AI research as complete without verification.
Anti-Hallucination Strategies:
1. Request Confidence Levels
Add to your prompts or custom instructions:
If you’re uncertain about any information, explicitly state your confidence level. For factual claims, indicate whether you’re citing specific sources or generalizing from training data.
2. Demand Source Attribution
When providing statistics, data, or specific claims, indicate where this information comes from or state clearly if you’re making informed estimates based on general knowledge.
3. Use Verification Prompts
After receiving information:
Review your previous response. Identify:
– Claims you’re most confident about (and why)
– Claims that should be independently verified
– Assumptions you made
– Areas where current/specific data would improve accuracy
4. Cross-Reference Critical Information
For important decisions or published content, verify key facts with authoritative sources. AI outputs are starting points, not final answers.
Human-in-the-Loop Workflow:
For Content:
- AI generates draft (handles 70-80% of work)
- You fact-check claims and statistics
- You add personal voice, examples, and insights
- You verify tone matches your brand
- You make final approval decision
For Business Decisions:
- AI provides analysis and recommendations
- You validate assumptions and data
- You consider factors AI can’t know (relationships, timing, intuition)
- You make the final call
For Research:
- AI compiles and synthesizes information
- You cross-reference key points with authoritative sources
- You note what’s verified vs. what’s AI inference
- You draw your own conclusions
Quality Control Checklist:
Create validation checklists for different output types:
Content Checklist:
- All statistics verified with sources
- Claims align with current information
- Tone and voice match my style
- No generic or obviously AI-sounding phrases
- Personal examples and insights added
- Proofreading complete
Business Analysis Checklist:
- Assumptions explicitly stated and validated
- Data sources identified or noted as estimates
- Recommendations consider my specific context
- Alternative perspectives considered
- Risks and limitations acknowledged
- Independent verification of key facts
Pro Tip: For high-stakes work, use two different AI tools independently and compare outputs. If ChatGPT and Claude give similar answers, confidence increases. If they differ significantly, that’s a signal requiring deeper investigation.
6. Common Challenges & Solutions
Expect these obstacles. Here’s how to handle them.
Challenge 1: Analysis Paralysis
The Problem: You’ve saved too many prompts and spend more time deciding which to use than actually working. Your prompt library becomes a procrastination tool.
The Solution:
The “Core 10” Rule: Identify the 10 tasks you do most frequently. Create ONE optimized prompt for each. Archive everything else.
Decision Framework: If you can’t decide which prompt to use in 30 seconds, you have too many options. Consolidate similar prompts.
Quick Start Document: Keep your top 5 most-used prompts in an easily accessible note. When in doubt, start there. Refinement can happen later—starting beats perfect planning.
Challenge 2: Overreliance on AI
The Problem: You haven’t had an original thought in weeks. Everything is AI-generated. Your unique voice is disappearing, and your work feels generic.
The Solution:
The 70-30 Rule: AI handles 70% of structure and drafting. You inject 30% of personality, insight, and originality.
Protection Strategy:
- Start ideation sessions WITHOUT AI (first 10 minutes is just you)
- Always add personal stories, examples, and opinions to AI content
- Use AI for process, not for thinking
- Reserve strategic decisions for human judgment
Reality Check Questions:
- Could anyone else have written this exact thing? (Red flag if yes)
- Does this sound like me? (Compare to your previous work)
- Am I challenging AI’s suggestions or accepting them blindly?
Weekly Exercise: Create something entirely without AI. Write, design, or strategize manually. This keeps your creative muscles sharp.

Challenge 3: Prompt Fatigue & Burnout
The Problem: You’re exhausted from constantly engineering perfect prompts. The optimization never ends. AI feels like another demanding task instead of a helpful tool.
The Solution:
Batch AI Work: Don’t context-switch constantly. Dedicate specific time blocks for AI tasks (e.g., 9-11 AM), and work normally outside those blocks.
Good Enough Rule: Stop optimizing prompts that already work adequately. If a prompt gets you 80% there in 2 minutes, that’s better than spending 20 minutes crafting perfection for 95% results.
AI-Free Days: Take regular breaks from AI to reset. Even one day per week without AI assistance can prevent burnout.
Time Limit: Set a timer. If you’ve been refining a prompt for more than 5 minutes, just run it. Iterate based on results, don’t endlessly theorize.

Challenge 4: Privacy & Ethical Concerns
The Problem: You’re worried about data privacy, becoming too dependent on AI, or ethical implications of AI-generated work.
Privacy Solutions:
- Never input confidential client information without permission
- Use anonymized examples when working with sensitive data
- Check your AI tool’s data policies (enterprise versions often have better privacy)
- For highly sensitive work, avoid AI entirely or use local models
Dependency Mitigation:
- Maintain manual skills—practice doing tasks without AI monthly
- Don’t let AI handle tasks you should personally master (core competencies)
- Think of AI as a bicycle (enhances capability) not a wheelchair (replaces it)
- Build systems that can function if AI becomes unavailable
Ethical Guidelines:
- Disclose AI use when required (academic, professional contexts)
- Take responsibility for all AI-generated outputs—your name is on it
- Don’t use AI to deceive or misrepresent
- Verify facts before publishing AI-researched content
- Credit human sources appropriately
The Transparency Rule: When someone asks “did AI write this?”, answer honestly: “AI helped with drafting and research. I provided strategy, editing, and final judgment.”
Quick Reference: Challenge Solutions
| Challenge | Immediate Action | Long-term Strategy |
| Analysis Paralysis | Use only your “Core 10” prompts | Quarterly library audit—delete ruthlessly |
| Overreliance | Apply 70-30 rule immediately | Weekly AI-free creative exercise |
| Burnout | Batch AI work to specific blocks | Schedule regular AI-free days |
| Privacy Concerns | Review data policies today | Develop personal AI ethics code |
Pro Tip: Create your personal “AI Ethics Statement.” Write down your boundaries and principles. Review it quarterly. This clarity eliminates decision fatigue around ethical questions and guides behavior when you’re uncertain.
7. Implementation: Your First Week with AI
Reading about AI productivity is worthless without action. Here’s your concrete 7-day implementation plan.
Day 1: Set Up Your Foundation (30 minutes)
Task 1: Choose Your Primary AI Tool
- Sign up for ChatGPT Plus, Claude Pro, or start with free versions
- Don’t overthink this—pick one and commit for 30 days
Task 2: Configure Custom Instructions
- Write your master prompt (use template from Section 2.2)
- Set your system preferences (use template from Section 2.3)
- Save both in your AI tool’s settings
Task 3: Create Your Prompt Library
- Open a new note in Notion, Google Docs, or your preferred tool
- Title it “AI Prompt Library”
- Create these categories: Content, Communication, Research, Planning, Analysis
Day 2: Audit Your Time (20 minutes)
Task: Track Everything
- Keep a simple log of every task you do today
- Note: Task name, Time spent, Frequency (daily/weekly/monthly)
- Mark which ones feel repetitive or time-consuming
- Identify your top 3 time-wasters
Day 3: Build Your First 3 Templates (45 minutes)
Task: Create Reusable Prompts
Based on yesterday’s audit, create templates for your 3 most frequent tasks.
Use this structure for each:
[TASK NAME] Template
Context: [Background info AI needs]
Task: [What you need]
Format: [How you want it structured]
Variables: [Things that change each time in BRACKETS]
Test each template once and refine if needed.
Day 4: Implement Daily Planning Routine (15 minutes)
Morning Planning Prompt:
Review my schedule and tasks for today [paste calendar + task list].
Priority goal: [your main objective for the day]
Available time: [your realistic work hours]
Provide:
– Time-blocked schedule
– Top 3 priorities ranked by impact
– Tasks to delegate or postpone
– Optimal focus time blocks
Use this prompt every morning this week. Adjust based on results.
Day 5: Automate One Workflow (30 minutes)
Task: Set Up Your First Automation
Choose ONE from these options:
Option A: Email Response Drafts
- Use ChatGPT or Claude to draft responses to common email types
- Save your 3 most common email templates
- Time saved: 30-60 minutes weekly
Option B: Meeting Summaries
- Sign up for Otter.ai or Fireflies (free tiers available)
- Record your next meeting
- Use AI to generate summary and action items
- Time saved: 15-30 minutes per meeting
Option C: Content Repurposing
- Take one piece of content you created
- Use AI to adapt it for 3 different platforms
- Save the repurposing prompt as a template
- Time saved: 45-90 minutes weekly
Day 6: Learn One New Skill (30 minutes)
Task: Use AI as Your Tutor
Pick something you’ve wanted to learn:
I want to learn [skill] to achieve [specific goal].
My current level: [beginner/intermediate/advanced]
Time available: 30 minutes daily
Create a 7-day learning plan including:
– Day-by-day topics to cover
– One practice exercise per day
– How to measure progress
– Resources to explore (if helpful)
Keep it practical—I want to apply this skill immediately.
Follow Day 1 of the plan today.
Day 7: Review and Optimize (20 minutes)
Reflection Prompt:
Here’s what I implemented this week with AI:
[List your activities and results]
Analyze:
– What worked best?
– Where did I struggle?
– What should I prioritize next week?
– What should I stop doing?
Suggest 3 specific improvements for my AI workflow.
Based on this analysis, adjust your approach for week 2.
Week 1 Results to Expect
Realistic outcomes:
- 2-4 hours saved through automation and templates
- Clearer daily priorities with less decision fatigue
- 3-5 reusable prompts that handle recurring tasks
- Basic comfort with AI tool and prompting
- One automated workflow running consistently
Don’t expect:
- Perfect outputs every time (you’ll still edit and refine)
- Complete transformation of how you work (that takes weeks)
- Zero learning curve (you’ll make mistakes—that’s normal)
Moving Beyond Week 1
Week 2-4 Focus:
- Add 2 more automation workflows
- Build your prompt library to 15-20 templates
- Create your first custom GPT (if using ChatGPT Plus)
- Implement AI for one major project
Month 2-3 Focus:
- Refine and optimize existing workflows
- Train team members on your AI systems
- Measure actual time savings with tracking
- Explore advanced techniques from Section 5
The Compound Effect:
Small consistent improvements compound dramatically:
- 1 hour saved daily = 260 hours annually (6.5 work weeks)
- 3 automated workflows = 5-8 hours weekly
- 20 prompt templates = 30+ minutes daily
Within 90 days, you’ll operate at a noticeably different level than peers who haven’t built these systems.
Conclusion
You now have a complete system for AI productivity: the frameworks, templates, workflows, and troubleshooting strategies that actually work.
But here’s what separates people who succeed from those who don’t: implementation bias.
Most readers will bookmark this guide, intend to apply it “when they have time,” and never start. A small percentage will implement one thing today and begin compounding advantages immediately.
Your Next Step (Choose One)
Don’t try to do everything. Pick ONE action right now:
Option 1: Quick Win (15 minutes) Set up custom instructions in your AI tool using the templates from Section 2. This immediately improves every future interaction.
Option 2: Template Creation (20 minutes)
Build one reusable prompt for a task you do at least weekly. Test it three times today and refine it.
Option 3: Automation Setup (30 minutes) Choose one repetitive task and set up a basic automation using Zapier or a similar tool.
Option 4: Start the 7-Day Plan Begin Day 1 of the implementation plan above. Commit to completing all seven days.
The Reality Check
AI won’t make you superhuman overnight. But used systematically over weeks and months, it creates genuine competitive advantages:
- You’ll produce more high-quality work in less time
- You’ll make better decisions with less cognitive load
- You’ll learn new skills faster than traditional methods allow
- You’ll reclaim hours weekly for strategic work or personal time
These benefits compound. The gap between you and non-adopters widens every week you maintain the system.
A Final Note
AI tools will evolve. Specific platforms will change. New features will emerge. But the principles in this guide—clear communication, systematic workflows, human validation, continuous refinement—remain constant.
Master these fundamentals now, and you’ll adapt easily as the technology advances.
Start small. Stay consistent. Measure results. Adjust based on what works for you specifically.
Your AI-powered productivity system begins with one action today.
FAQ: Common Questions About AI Productivity
How long does it take to see results?
Short answer: You’ll see immediate time savings (minutes to hours) within the first week. Significant productivity improvements appear within 3-4 weeks of consistent use.
Detailed answer:
- Days 1-7: Small wins like faster email drafting, better daily planning (2-4 hours saved weekly)
- Weeks 2-4: Noticeable efficiency gains as templates and workflows become habits (5-8 hours saved weekly)
- Months 2-3: Compound effects kick in—multiple automated workflows, refined prompts, integrated systems (10-15 hours saved weekly)
The key variable is consistency. This means daily users see results faster than occasional users.
Do I need technical skills or coding knowledge?
No. The strategies in this guide require zero technical knowledge.
You need three things:
- Ability to write clear instructions hence (if you can send a detailed email, you’re qualified)
- Willingness to experiment and learn from mistakes
- Consistency in using AI for 15-30 minutes daily
Tools like ChatGPT, Claude, and Zapier are designed for non-technical users. Everything operates through plain English conversation or simple drag-and-drop interfaces.
The learning curve is shorter than learning Excel or PowerPoint was.
Which AI tool should I start with?
For most people: ChatGPT
Reasoning:
- Intuitive interface with low learning curve
- Strong general-purpose capabilities across most tasks
- Large community providing support and shared prompts
- Custom GPTs feature (in Plus tier) adds significant value
- Free tier available for testing before paid commitment
Alternatives to consider:
- Claude: Better for nuanced writing, complex analysis, and longer documents
- Gemini: Best if you work heavily in Google Workspace
- Jasper: Specialized for marketing content creation
Strategy: Start with one tool. Use it daily for 30 days. Learn it deeply before exploring alternatives. Tool-hopping prevents mastery.
Free tiers work fine for learning. Upgrade to paid versions ($20-30/month) once you’re consistently hitting usage limits.
How do I avoid AI making mistakes or “hallucinating”?
Use these validation layers:
1. Request Confidence Indicators Add to prompts: “State your confidence level for factual claims and indicate whether you’re citing specific sources or generalizing.”
2. Cross-Reference Critical Information Never publish important facts without verification from authoritative sources. Treat AI outputs as first drafts requiring validation.
3. Use Multiple Tools for Important Work Run critical analyses through both ChatGPT and Claude. Agreement increases confidence; disagreement signals need for deeper investigation.
4. Implement Human Review Always review AI outputs before using them. Add your expertise, check logic, verify facts, inject personal voice.
5. Include Verification Prompts After receiving information: “Review your response. Identify claims needing independent verification and state any assumptions you made.”
The Rule: AI proposes, humans validate and decide. Your judgment and expertise remain essential.
Can AI replace my job?
Short answer: AI replaces tasks, not entire jobs. It makes some roles obsolete while creating demand for new ones.
Realistic perspective:
What AI handles well:
- Repetitive tasks following clear patterns
- First drafts of content, code, analysis
- Data processing and synthesis
- Routine communication
- Research compilation
What AI can’t replace:
- Strategic thinking requiring business context
- Relationship building and emotional intelligence
- Creative direction and taste judgment
- Ethical decision-making
- Navigating organizational politics
- Adapting to novel, undefined problems
The actual risk: Not AI replacing your job, but someone using AI to do your job better than you.
The opportunity: Using AI to become more valuable by focusing on high-level strategy, relationship work, and creative problem-solving while AI handles execution and routine tasks.
People who augment their skills with AI will replace people who don’t, not the AI itself.
Is my data safe when using AI tools?
It depends on which tool and how you use it.
Free versions (ChatGPT, Claude):
- Conversations may be used for training (check current policies)
- Don’t input confidential client information, proprietary data, or personal identifying information
Paid/Enterprise versions:
- Generally offer better privacy protections
- Data typically not used for training
- Check specific privacy policies for your tool
Best practices:
- Read privacy policies before using AI tools professionally
- Anonymize sensitive information (use “Company A” instead of real names)
- Never input passwords, financial data, or legal documents without proper protections
- For highly confidential work, use enterprise versions or avoid AI entirely
- Consider local AI models for sensitive use cases
For most productivity applications (drafting emails, planning tasks, learning skills), privacy risk is minimal if you avoid inputting confidential information.
How much time should I spend on AI daily?
Starting phase (Weeks 1-4): 30-45 minutes daily
- Learning how to prompt effectively
- Building your template library
- Setting up workflows
- Experimenting with different approaches
Maintenance phase (After month 1): 15-30 minutes daily
- Using established templates and workflows
- Most AI interactions take 2-5 minutes each
- Systems run increasingly on automation
The goal isn’t to spend more time with AI—it’s to spend less time on work overall.
Once systems are established, AI operates in the background. You interact with it briefly throughout the day (quick prompts, automated workflows) rather than dedicating large blocks of time.
Red flag: If you’re spending 2+ hours daily crafting prompts, you’re over-optimizing. Simplify your approach.
What if AI gives me generic or unhelpful responses?
This almost always indicates prompt issues, not AI limitations.
Common causes and fixes:
Problem: Vague prompts
- ❌ “Help me with marketing”
- ✅ “Create 3 LinkedIn post ideas about AI productivity for B2B SaaS founders, each with a contrarian angle”
Problem: Missing context
- ❌ “Write an email to this client”
- ✅ “Draft a 150-word follow-up email to a client who’s gone silent for 2 weeks. Tone: concerned but not pushy. Goal: re-engage without pressure.”
Problem: No format specification
- ❌ “Analyze this data”
- ✅ “Analyze this data and present as: 3 key insights with supporting evidence, 2 surprising patterns, 1 recommended action. Use bullet points.”
Problem: Generic system instructions
- ❌ Default settings
- ✅ Custom instructions specifying your role, preferences, and constraints
Solution: Use the frameworks from Section 2. Include role, context, format, constraints, and success criteria in your prompts.
If outputs remain generic after improving prompts, you may need a more advanced model (GPT-4 vs GPT-3.5) or different tool.
Can teams or companies use these strategies?
Yes, and it’s often more powerful at the team level.
Team implementation approach:
Phase 1: Individual Adoption (Week 1-2)
- Have team members complete the 7-day implementation plan individually
- Share results and best practices in team meetings
- Identify which workflows apply to multiple people
Phase 2: Shared Systems (Week 3-4)
- Create team prompt library with templates everyone uses
- Build shared custom GPTs for common team tasks
- Establish quality control standards for AI outputs
Phase 3: Process Integration (Month 2+)
- Integrate AI into standard operating procedures
- Automate team workflows (meeting summaries, status updates, etc.)
- Train new team members on established AI systems
Benefits of team adoption:
- Shared template libraries reduce redundant work
- Consistent quality across team outputs
- Faster onboarding for new members
- Compound time savings across multiple people
Management considerations:
- Set clear policies on AI use (what’s acceptable, what’s not)
- Address privacy and confidentiality concerns explicitly
- Establish human review requirements for different work types
- Measure and track team productivity improvements
Many companies report 20-30% efficiency gains when teams adopt AI systematically versus individuals using it ad hoc.
Additional Resources
Prompt Libraries:
- Anthropic’s Prompt Library (for Claude)
- OpenAI’s Prompt Engineering Guide
- Community-driven prompt sharing platforms
Automation Tools:
- Zapier (connects 5,000+ apps with AI)
- Make (formerly Integromat—advanced automation)
- IFTTT (simple task automation)
AI Tool Directories:
- There’s An AI For That (searchable database)
- Future Tools (curated AI tool reviews)
- AI Tool Hub (categorized by use case)
Continued Learning:
- Anthropic documentation (for Claude)
- OpenAI documentation (for ChatGPT)
- AI productivity communities on Reddit, Discord
Tracking & Measurement:
- RescueTime (tracks time saved)
- Toggl Track (time tracking with AI integration)
- Simple spreadsheet tracking your before/after metrics
The best AI productivity system is the one you’ll actually use consistently. So, start simple, build habits, and then expand. Your future self will thank you for starting today.

